As an acronym of Content Management System, a CMS operates to ease the creation, storage, editing and publication of content on a website. It does not demand its users to write numerous codes, therefore the layout, change, and even design of websites can be done easily. A CMS is the centralised system where content is created, edited, collaborated, and disseminated to users, and it is made up of two systems namely;
1. Content Management Application (CMA)
The Content Management Application (CMA) is a graphical user interface or the front end where people who do not know how to program can develop, publish and manage contents. It also works as the operating panel that the user gets to interact with when it comes to the management of the website using the CMS.
How the CMA Works
Content publication: As with text editing, writing content is quite simple and easy, coming as it does with a full featured text editor similar to MS Word/ Google docs where you can write blogs, Web Pages, product listing, multi media content etc.
- Website Editing and Formatting Tool: The CMA presents a WYSIWYG option by which users can modify texts, structures, add images and videos and apply styles, among others, with no need of programming.
- Media Management: Referencing of images, videos and other documents is easy in that users can upload and sort them in a particular media tab. These files can then be deployed to web pages easily with few clicks, developers can make changes as well as edit these files.
- Scheduling: Most of the CMS platforms come with scheduling systems where people can set the required dates upon which contents will be published hence avail them on time.
- Personalization: These are builders where one can drag an object, -drop it to see where it will be placed in the website and do not need to know HTML or CSS to do this.
Compared to other content management systems, the CMA can be used by anybody ranging from a blogger to the owners of a business enterprise and thus enables them to update their site with a lot of ease.
2. Content Delivery Application (CDA)
As seen, the Content Delivery Application (CDA) is the back-end application that holds, processes and disseminates the content generated in the CMA to the website consumers. This component makes certain that each of the web components, which makes up the site, loads efficiently and works to the best of its capabilities.
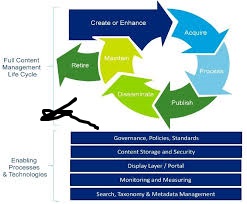
How the CDA Works
Data Storage At CMA: As noted, when users create content, they are actually stored in a structured database. Whenever one visits this website, the CDA is programmed to pull this data out.
- Content Retrieval: What happens when a visitor gets to the web page the CDA uses database and brings the appropriate content to build the web page at the same instance.
- Display: The system takes care of the text and producing bitmap or raster graphics, that is; the pictures, videos, audios, documents and all other media to ensure that they are properly formatted to appear as intended on any device or browser that they are viewed on.
- Website Optimization: The CDA adds functionality to the website by managing and storing web content, handling images, and data responsibilities.
- Security and Updates: The back end also incorporates security measures such as firewalls for website security , user login and encryption for user content.
Each component of the CDA can go unnoticed but has the overall mandate of making the website fast and secure for everyone.